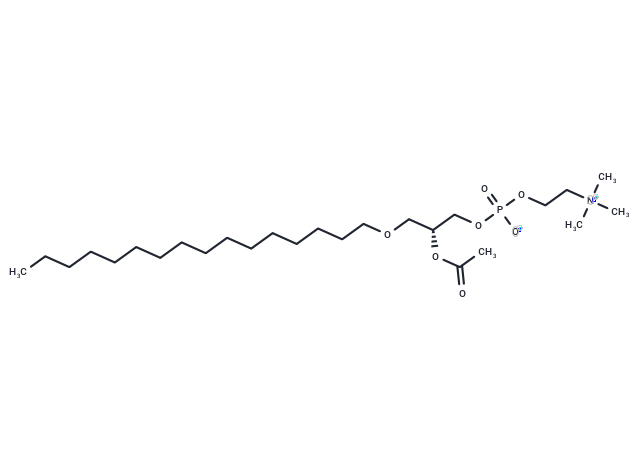
PAF (C16)
CAS No. 74389-68-7
PAF (C16)( —— )
Catalog No. M33743 CAS No. 74389-68-7
PAF (C16) is a potent MAPK and MEK/ERK activator that induces increased vascular permeability. PAF (C16) (PAF (C16)) is a platelet-activating factor, a phospholipid-derived mediator and a ligand for PAF G protein-coupled receptor (PAFR). PAF (C16) has shown anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory activity in vitro, inhibiting Caspase-dependent apoptosis by interacting with its receptor (PAF-R) to perform cell signaling.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 105 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePAF (C16)
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPAF (C16) is a potent MAPK and MEK/ERK activator that induces increased vascular permeability. PAF (C16) (PAF (C16)) is a platelet-activating factor, a phospholipid-derived mediator and a ligand for PAF G protein-coupled receptor (PAFR). PAF (C16) has shown anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory activity in vitro, inhibiting Caspase-dependent apoptosis by interacting with its receptor (PAF-R) to perform cell signaling.
-
DescriptionC16-PAF (PAF (C16)), a phospholipid mediator, is a platelet-activating factor and ligand for PAF G-protein-coupled receptor (PAFR). C16-PAF exhibits anti-apoptotic effect and inhibits caspase-dependent death by activating the PAFR. C16-PAF is a potent MAPK and MEK/ERK activator. C16-PAF induces increased vascular permeability.
-
In VitroC16-PAF (PAF (C16); 0.5-1.5 μM; for 24 hours) elicits significant concentration-dependent neuronal loss in PAFR but not PAFR+/+ cultures. C16-PAF (1 μM) elicits neuronal death in PAFR cells infected with EGFP alone. C16-PAF (1 μM; for 24 hours) activates caspase 7 but not caspase 3 in PAFR neurons.C16-PAF is synthesized by two distinct pathways; the remodeling pathway and the de novo synthesis pathway. C16-PAF acts by binding to a unique G-protein-coupled seven transmembrane receptor.C16-PAF (1-25 μg/ml; 6, 12, 24 h) inhibits M. smegmatis and M. bovis BCG growth in a time-dependent manner.Cell Viability Assay Cell Line: Cerebellar granule neurons (CGNs) from PAFR?/? and PAFR+/+ mice Concentration:0.5-1.5 μM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Elicited significant concentration-dependent neuronal loss in PAFR?/? but not PAFR+/+ cultures in serum-free media.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:CGNs Concentration:1 μM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Activated caspase 7 but not caspase 3 in PAFR?/? neurons.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMAPK/ERK Signaling
-
Targetp38 MAPK
-
RecptorMAPK | MEK | Endogenous Metabolite | ERK
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number74389-68-7
-
Formula Weight523.68
-
Molecular FormulaC26H54NO7P
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (95.48 mM; Ultrasonic (<60°C); )H2O : 33.33 mg/mL (63.65 mM; Ultrasonic)
-
SMILES[C@H](COP(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)(=O)[O-])(COCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)OC(C)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Scott D Ryan, et al. Heterogeneity in the sn-1 carbon chain of platelet-activating factor glycerophospholipids determines pro- or anti-apoptotic signaling in primary neurons. J Lipid Res. 2008 Oct;49(10):2250-8.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
PH797804
PH-797804 is a novel pyridinone inhibitor of p38α with IC50 of 26 nM in a cell-free assay; 4-fold more selective versus p38β and does not inhibit JNK2. Phase 2.
-
Maohuoside A
Maohuoside A promotes osteogenesis of rat mesenchymal stem cells via BMP and MAPK signaling pathways.
-
SD 169
SD 169 is a selective and ATP competitive the MAP kinases p38α and p38β?inhibitor.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


